Mappings to UDP/IP v4&6, Ethernet (direct mapping), DeviceNetTM, PROFINET, ControlNetTM
Optional unicast messaging (in addition to multicast)
Formal mechanisms for message extensions (using TLV)
PTP profiles
Transparent clocks
Configuration options
Synchronization accuracies better than 1 ns
Security (experimental specification only)
- Covered very briefly in this tutorial
- See reference 6 for more information
Options for redundancy and fault tolerance
Means to accumulate cumulative frequency scale factor offset relative to grandmaster
(experimental specification only)
New management capabilities and options
Higher sampling rates compared to V1; asymmetry corrections

PTP clock types
P2P TC
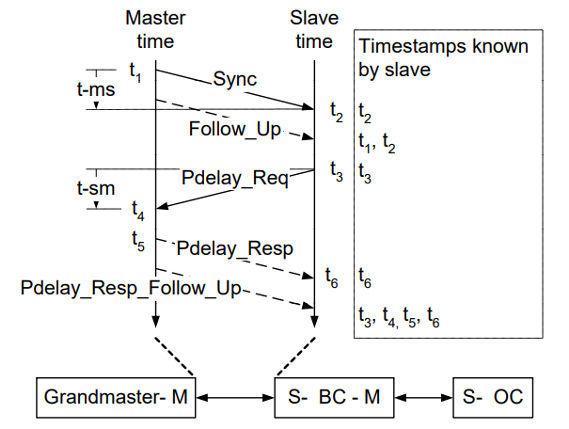
Peer-to-peer transparent clock (P2P TC): A transparent clock that, in addition to providing PTP event transit time information, also provides corrections for the propagation delay of the link connected to the port receiving the PTP event message. In the presence of peer-to-peer transparent clocks, delay measurements between slave clocks and the master clock are performed using the peer delay measurement mechanism.
E2E TC
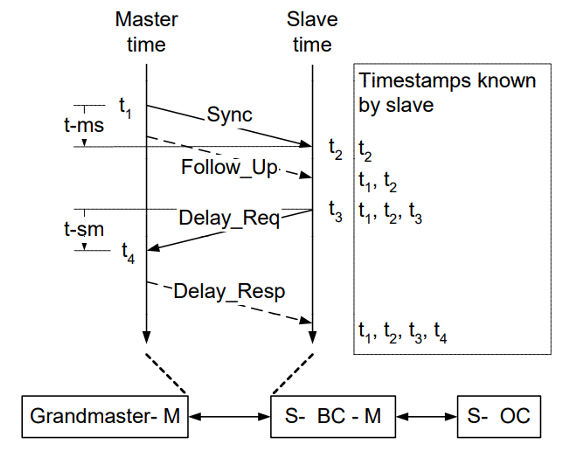
End-to-end transparent clock (E2E TC): A device that only measures the time taken for a PTP event message to transit the device and provides this information to clocks receiving this PTP event message; i.e., it does not provide corrections for the propagation delay of the link connected to the port receiving the PTP event message. It does not use the peer delay measurement mechanism but, instead, supports use of the delay request-response mechanism
PTP event messages
PTP general messages
PTP communication path